The Story
If you’ve ever managed servers, you should know that there are some metrics that you should keep an eye on. AWS automatically sets you up with some metrics, such as CPU Utilization, network in/out, and status checks. However, there are still some very important metrics that are missing: memory utilization and disk usage.
Finding out how to set up the collection of these metrics was easy enough. A quick Google search, first result, and there’s documentation on AWS giving a detailed step by step guide on how to do this. That all went well. However, having metrics without alarms was kind of useless. No one is going to stare at the graphs 24/7. So, creating alarms was the natural next step. Usually, this is a simple affair, assuming the source of the metrics never change.
You see, AWS alarms require that the source of the metrics be fully defined. But since your metrics should be well organized, you would want to put these metrics inside namespaces, which are further defined with things like the instance ID, the name of the disk, and the actual memory/disk usage itself.
If your EC2s are controlled by auto scaling groups, then your instance IDs are always changing. This means that a manually created alarm is going to become irrelevant once the EC2 is terminated, and new instances will not have any alarms. You could get around this by dropping the instance ID from the metric, but then you wouldn’t know which instance the alarm is ringing for.
So, the solution is to create these alarms automatically when an instance is started, and delete these alarms when an instance is terminated. This will be what I’ll be focusing on in this guide.
Monitoring
I’ll briefly cover this a bit, just to make this guide a little more complete.
To get monitoring set up, you’ll need to install the CloudWatch Agent on your EC2s in order to get the memory and disk usage of your instance.
Since there’s a very well written guide on AWS, I’ll just link it here instead of rephrasing everything it says. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/Install-CloudWatch-Agent.html
I recommend that you use the following CloudWatch Agent configuration, and it strips away most of the clutter, especially when it comes to disk metrics. Do note that this configuration will only report the disk usage of non-system disks. Feel free to change the collection interval (unit in seconds).
{
"agent": {
"metrics_collection_interval": 300,
"run_as_user": "root"
},
"metrics": {
"append_dimensions": {
"AutoScalingGroupName": "${aws:AutoScalingGroupName}",
"InstanceId": "${aws:InstanceId}"
},
"metrics_collected": {
"disk": {
"measurement": [
"used_percent"
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 300,
"resources": [
"*"
],
"drop_device": true,
"ignore_file_system_types": ["devtmpfs", "squashfs", "tmpfs"]
},
"mem": {
"measurement": [
"mem_used_percent"
],
"metrics_collection_interval": 300
}
}
}
}
Alarms
First, I’m going to assume that you know how to create alarms manually. I’ll be diving straight into managing these automatically.
Now, these are the steps you’ll need to carry out to get the automatic creation/deletion of alarms working:
- Set up the lifecycle hooks.
- Create an AWS Lambda function to process the lifecycle hooks, and create/delete alarms.
- Create an EventBridge rule to forward the lifecycle event to the AWS Lambda function.
Set up the lifecycle hooks
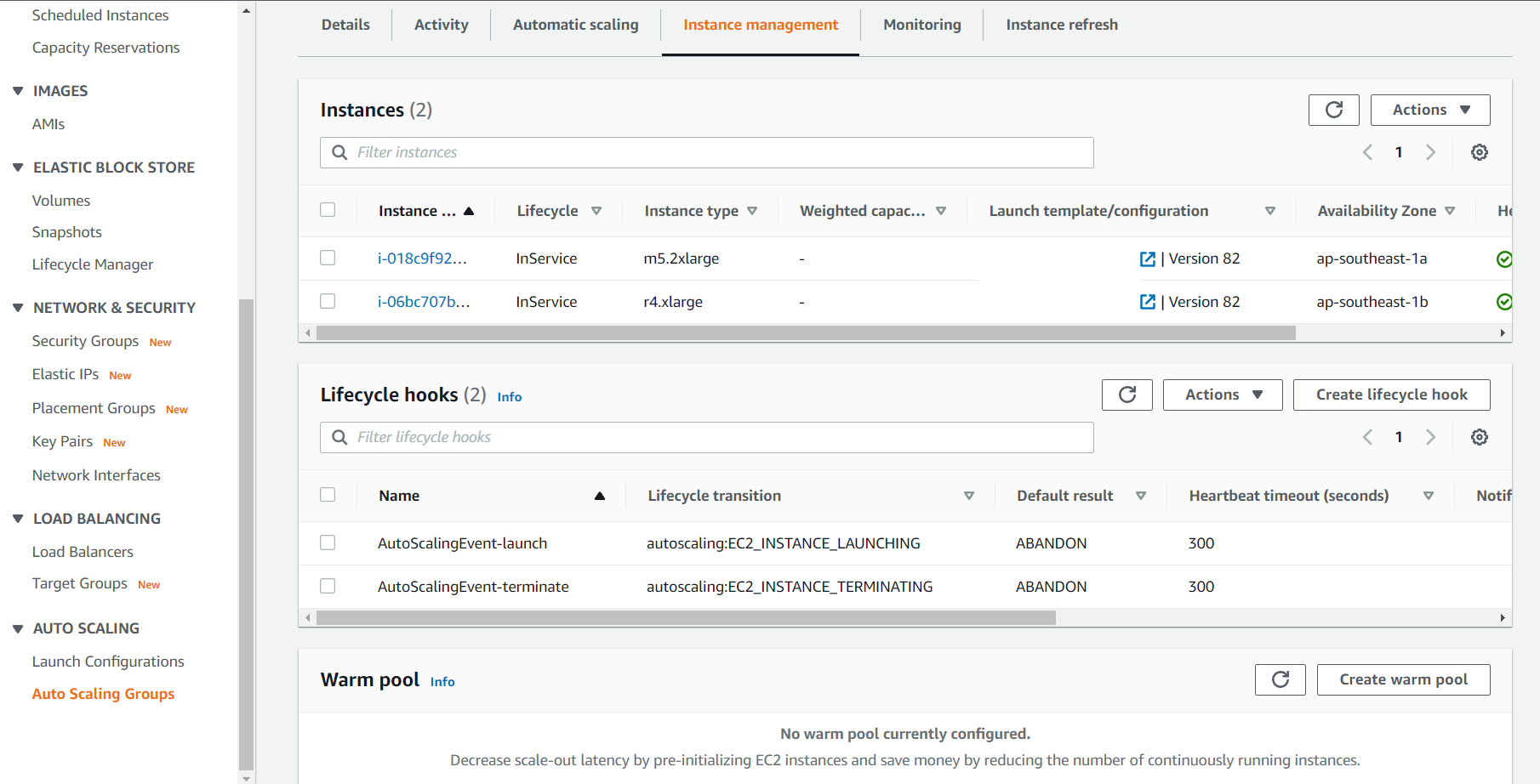
From your EC2 Auto Scaling Groups page, select your auto scaling group, and go to the “Instance management” tab. Find the “Lifecycle hooks” section, and create two lifecycle hooks - one for “Instance launch”, and one for “Instance terminate”. Reduce the heartbeat timeout to something more appropriate, as I find the default of 3600 seconds rather ridiculous.
Create a Lambda Function
You’ll need to create a lambda function to receive and process the lifecycle hooks, and to create/delete the alarms.
Go to the AWS Lambda page, and create a function, authoring it from scratch. I will be providing a basic template of how to handle the lifecycle hooks, and perform a creation and deletion of a disk usage alarm. The code to do the same for memory usage is left as an exercise to the reader :D
In general, here’s what the function will be doing:
- Receive the lifecycle hook event, and mark it as complete. This needs to be done or the auto scaling group action will not continue.
- Extract the lifecycle action and instance details from the event.
- If it is an instance start event, create the necessary alarms.
- If it is an instance termination event, delete the respective alarms.
You will need to create a role for your lambda function that has the permissions to create and delete alarms. I will not be covering how to do this.
Here’s the code using Python 3:
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Initialize the boto3 client to use the AWS SDK.
asg = boto3.client('autoscaling')
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
# The event object contains details about the auto scaling event.
eventDetail = event['detail']
# You'll need to complete the lifecycle action so that the auto scaling action can continue.
# https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/autoscaling.html#AutoScaling.Client.complete_lifecycle_action
response = asg.complete_lifecycle_action(
LifecycleHookName = eventDetail['LifecycleHookName'],
AutoScalingGroupName = eventDetail['AutoScalingGroupName'],
LifecycleActionToken = eventDetail['LifecycleActionToken'],
LifecycleActionResult = 'CONTINUE',
InstanceId = eventDetail['EC2InstanceId'],
)
# We'll be using these details to name our alarms
instanceId = eventDetail['EC2InstanceId']
autoScalingGroupName = eventDetail['AutoScalingGroupName']
autoScalingGroupAction = eventDetail['LifecycleTransition']
if autoScalingGroupAction == 'autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_LAUNCHING':
# Create DiskUsage alarm for newly launched instance
# https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/cloudwatch.html#CloudWatch.Client.put_metric_alarm
response = cloudwatch.put_metric_alarm(
AlarmName='DiskUsage-' + instanceId,
AlarmDescription='DiskUsage exceeds 85%% for ' + instanceId,
MetricName='disk_used_percent',
Namespace='CWAgent',
Statistic='Average',
Dimensions=[
{
'Name': 'InstanceId',
'Value': instanceId
},
{
'Name': 'AutoScalingGroupName',
'Value': autoScalingGroupName
},
{
'Name': 'path',
'Value': '/'
},
{
'Name': 'fstype',
'Value': 'ext4'
}
],
Period=300,
EvaluationPeriods=1,
Threshold=85,
ComparisonOperator='GreaterThanThreshold',
AlarmActions=[
# Replace the line below with the target ARN for your alarm notification.
# For example, you might be using AWS SNS to notify certain emails or a Slack channel.
# Put the ARN of the SNS topic here.
'arn:aws:sns:region:account-id:sns-topic-name'
]
)
elif autoScalingGroupAction == 'autoscaling:EC2_INSTANCE_TERMINATING':
# Delete DiskUsage alarm of terminated instance
# https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/cloudwatch.html#CloudWatch.Client.delete_alarms
response = cloudwatch.delete_alarms(
AlarmNames=['DiskUsage-' + instanceId]
)
return response
Deploy the lambda function by pressing the “Deploy” button.
Create an EventBridge rule
You’ll need this EventBridge rule to capture the lifecycle hooks, and to forward it to something that can use the hooks.
EventBridge rules are accessible from both CloudWatch and the EventBridge page.
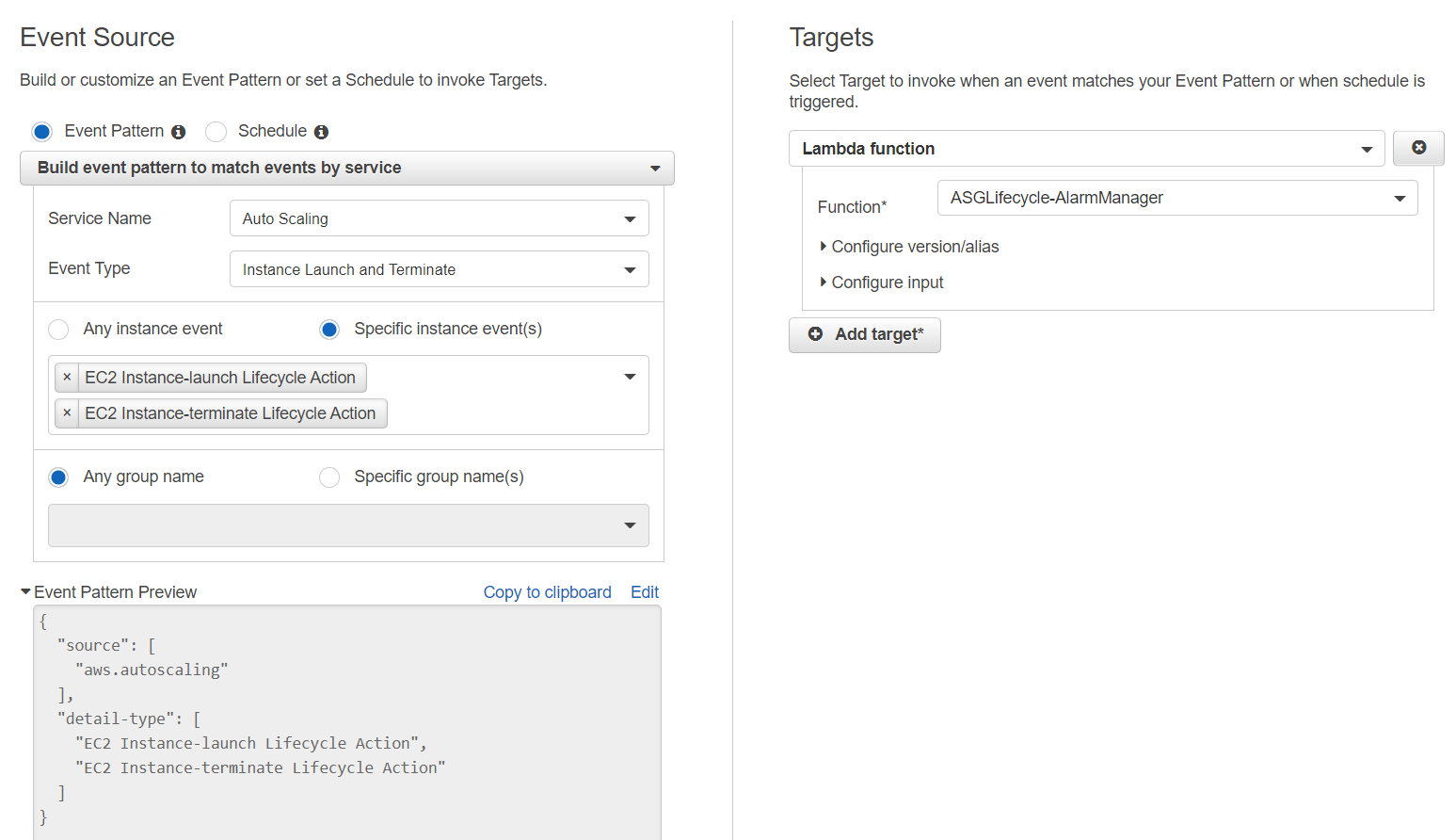
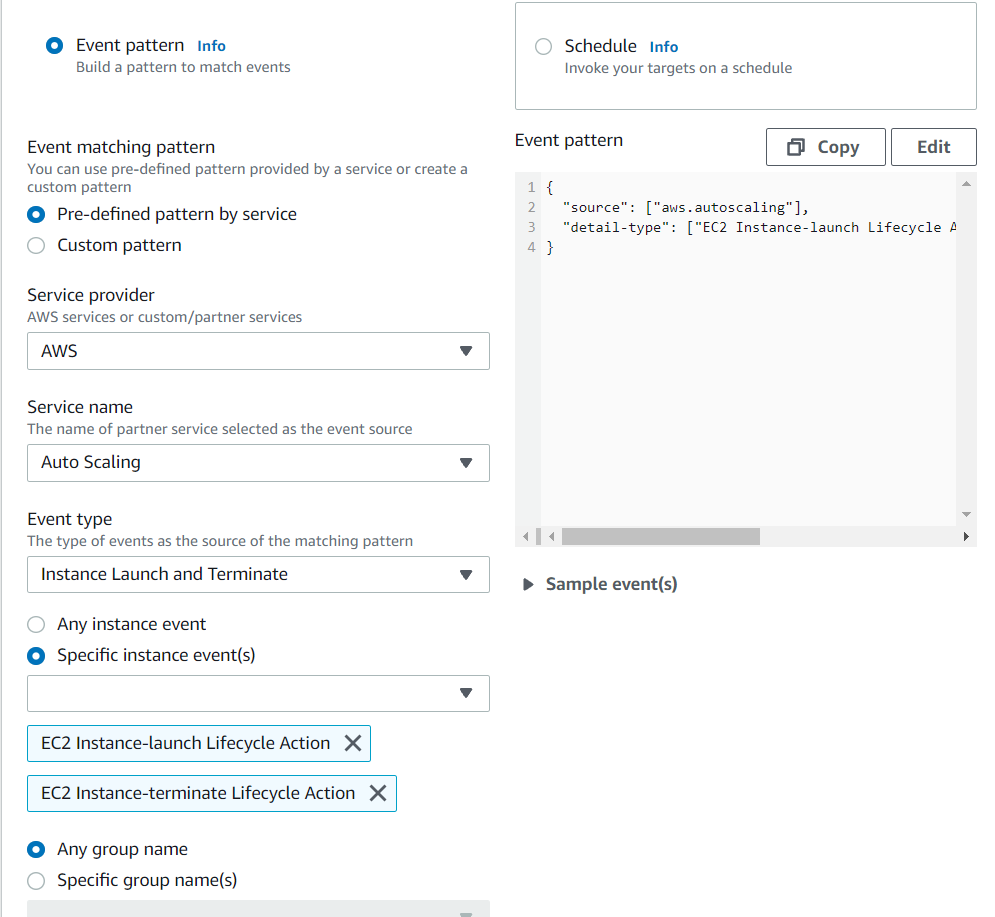
You’ll want to choose these options:
- “Event Pattern” type
- Match events by service (CloudWatch UI)/Pre-defined pattern by service (EventBridge UI)
- Service provider: AWS (ignore this if using CloudWatch UI)
- Service name: Auto Scaling
- Event type: Instance Launch and Terminate
- Specific instance events: choose the two lifecycle actions you created previously
- Any group name
- Event Pattern:
{ "source": [ "aws.autoscaling" ], "detail-type": [ "EC2 Instance-launch Lifecycle Action", "EC2 Instance-terminate Lifecycle Action" ] } - Target: Lambda Function
- Function: The lambda function you created previously.
This UI is from CloudWatch:
This UI is from EventBridge:
That’s It
And that’s it! You should have fully functional alarms that create and delete themselves with EC2 starting and termination. Fuss free, automatic, and it should work all the time.
Comments